Well, you can now stop holding your breath (you've got your mask on, right?!), 'cause here it is!
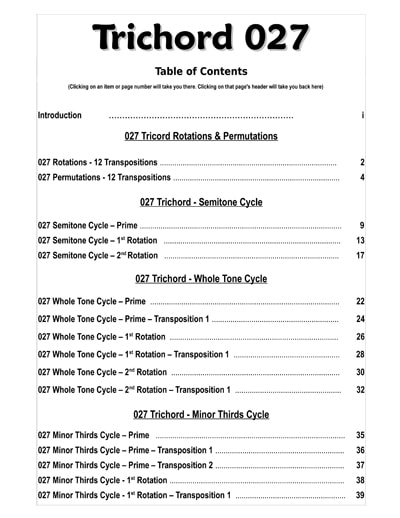
With the straightforward, no nonsense title "Trichord 027", this new volume features all of 111 pages of introductory to advanced exercises, sequences and melodic lines, based on combinations and permutations of this familiar, contemporary sound.
The close relationship of the 027 Trichord with both the interval of a Perfect 4th and the Pentatonic Scale is highlighted in this volume, as is its symmetry within a 12-Tone Row.
Ex. 1 – Ascending 027 Trichord from C, in Prime, 1st & 2nd Rotations (12 transpositions)
Each Trichord has 3 expressions known as rotations and likened to inversions in a traditional triad. They are:
Prime 1st Rotation 2nd Rotation
Ex. 2 – 027 Melodic Permutations and Retrograde from C (12 transpositions)

All cycle exercises throughout the book are presented in Retrograde, as well.


The Minor 3rds Cycle is unique in that any rotation of 027 as a full cycle results in a 12-tone row (see Ex. 10 & 11, as well as 6 & 7 below).

Ascending direction 027 trichords in Prime Form.

Ascending direction 027 trichords in 1st Rotation.
Any pair of 027 Trichords a Major 3rd apart, forms a traditional Maj7 #11 chord, when expressed in 3rds (CDG & E-F#-B = C-E-G-B-D-F# = C Maj7 9 #11).
The use of 027s with any of the aforementioned cycles creates a sense of temporary key modulation – or “inside / outside / inside” melodic and harmonic movement.
Examples of practical usage are presented as 4-bar sequences, with a target resolution usually within the final two measures. As no chord symbols are given, the resolution could be to any quality chord within that defined tonality.
A description of the 027s used in the two lines below is labeled in prime under each example, along with its rotation - 1 or 2 (x = permutation).
As the relationship between 027, the interval of a perfect 4th and the Pentatonic Scale is interwoven and inseparable, actual and overlapping pentatonics are noted in parentheses.
Ex. 8 – Four-bar 027 Sequence resolving to C (#1)
(A & E Pentatonics) (G#, D# & F# Pentatonics)
The combined cycle relationships between the trichords which comprise the line in Ex. 8 (above) turn out to be as follows:
Maj 3rd – Whole-Tone – min 3rd – tritone – Maj 3rd - Whole-Tone – Maj 3rd – semitone - (tritone)
And in Ex. 9 (below):
min 3rd – min 3rd – min 3rd – Maj 3rd – semitone – min 3rd – (min 3rd).
Ex. 9 – Four-bar 027 Sequence resolving to C (#2)
(Bb & Eb Pentatonic) (E & A Pentatonic)
The interval distance (in brackets, between trichords) in which the first note of each trichord is spaced is known as its steering. There are 3 basic steerings for 027: 1+2, 2+4 and 3+3
.
Ex. 10 – 027 Rows & Steerings: Row I (2+5, 5+2), Steering 1+2
Ex. 11 – Lines from the Row
The 027 Trichord is a powerful tool for the improviser. Command of it will take one into fresh territory not realized through triadic harmony and “scale running” alone.
B. Stern


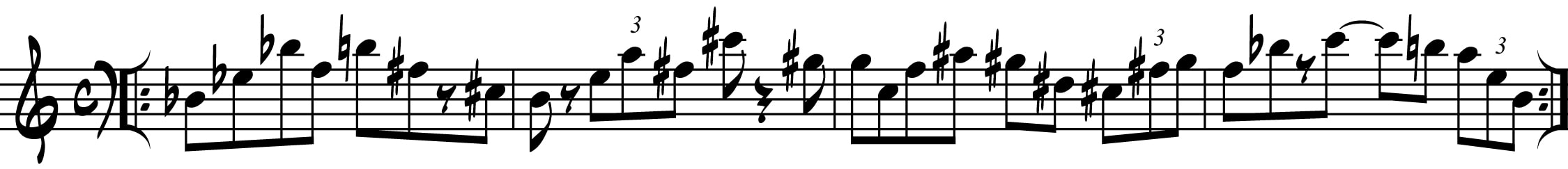







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed









